Learn More
Invitrogen™ iNOS Recombinant Rat Monoclonal Antibody (CXNFT), Invitrogen™
Rat Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Brand: Invitrogen™ 740025T
Description
Recombinant Rat monoclonal antibodies are produced using in vitro expression systems. Recombinant antibodies are produced using specific genes that code for the desired antibodies. These genes are cloned into an expression vector and expressed in vitro. The advantages of recombinant antibodies include better specificity and lot-to-lot consistency. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
iNOS (Inducible Nitric oxide, NO, NOS) is an inorganic, gaseous free radical that carries a variety of messages between cells. Vasorelaxation, neurotransmission and cytotoxicity can all be potentiated through cellular response to NO. NO production is mediated by members of the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) family. iNOS is expressed in liver and inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines. NOS catalyzes the oxidization of L-arginine to produce L-citrulline and NO. Two constitutive isoforms, brain or neuronal NOS (b or nNOS, type I) and endothelial cell NOS (eNOS, type III), and one inducible isoform (iNOS, type II), have been cloned. All NOS isoforms contain calmodulin, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and flavin mononucleotide (FMN) binding domains. iNOS is found in a variety of cell types including macrophages, hepatocytes, synoviocytes, and smooth muscle cells. Cytokines such as interferon-gamma (IFN), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1 and -2, and lipopolysaccarides (LPS) cause an increase in iNOS mRNA, protein, and activity levels. Protein kinase C-stimulating agents exhibit the same effect on iNOS activity. After cytokine induction, iNOS exhibits a delayed activity response which is then followed by a significant increase in NO production over a long period of time. Three related iNOS pseudogenes are located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Diseases associated with iNOS dysfunction include achalasia and impotence.
Specifications
| iNOS | |
| Recombinant Monoclonal | |
| 1.0 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| P29477 | |
| Nos2 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 18126 | |
| Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles. | |
| Liquid |
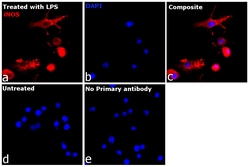
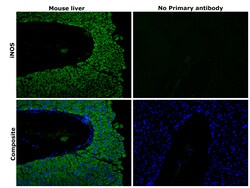
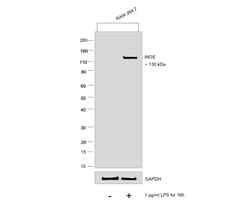
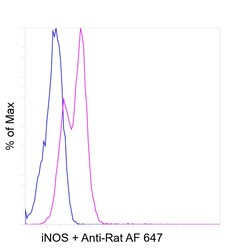
| Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry | |
| CXNFT | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Nos2 | |
| Hepatocyte NOS; hepatocytes; HEP-NOS; inducible nitric oxide synthase; inducible NO synthase; Inducible NOS; iNos; i-NOS; Inosl; MAC-NOS; macrophage NOS; nitric oxide synthase 2; nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible; nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible, macrophage; nitric oxide synthase 2A (inducible, hepatocytes); nitric oxide synthase, inducible; nitric oxide synthase, macrophage; nitric oxide synthase-inducible; NOS; NOS type II; NOS, type II; Nos2; Nos-2; Nos2a; NOS-II; OTTMUSP00000000202; peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS2 | |
| Rat | |
| 100 μL | |
| Primary | |
| Mouse | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG2a κ |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.