Learn More
Eurofins DiscoverX PKA Protein, Recombinant

Description
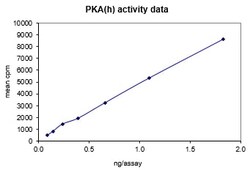
Cyclic-AMP exerts its effects in animal cells mainly by activating the enzyme cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA). This enzyme catalyzes transfer of the terminal phosphate group from ATP to specific serines and threonines of selected proteins. Covalent phosphorylation of the appropriate amino acids of specific cellular proteins in turn results in altered cellullar function as a consequence of activation or inactivation of enzymes or altered membrane permeability to ions or other possible effects. PKA is found in all animal cells, and it is known that hormones or transmitters may be mediated by cAMP-stimulated phosphorylation of specific sites on neuronal or non-neuronal cells to exert their physiological function.
GenBank X07767
Specifications
Specifications
| Formulation | mg/mL of enzyme in 30 mM potassium phosphate pH 7.4, 150 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 50% glycerol. Frozen solution. |
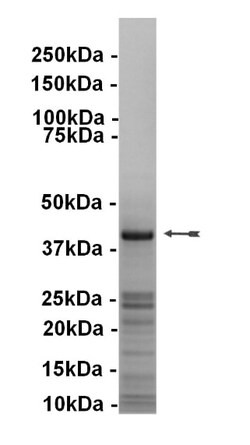
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 41 kDa |
| Quantity | 10 μg |
| Species | Human |
| Recombinant | Recombinant |
| Protein Tag | Untagged |
| Expression System | Recombinant enzyme expressed in E. coli cells |
| Protein Form | Full-length |
| Purity or Quality Grade | ≥59% |
| Protein | PKA, catalytic subunit, recombinant |
The Fisher Scientific Encompass Program offers items which are not part of our distribution portfolio. These products typically do not have pictures or detailed descriptions. However, we are committed to improving your shopping experience. Please use the form below to provide feedback related to the content on this product.