Learn More
PeproTech FGF23 Polyclonal Antibody, Biotin, PeproTech®, Invitrogen™
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Brand: PeproTech 500-P319BT-50UG
Description
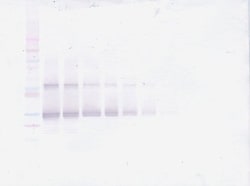
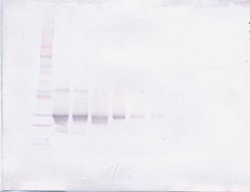
AA Sequence of recombinant protein: MYPNASPLLG SSWGGLIHLY TATARNSYHL QIHKNGHVDG APHQTIYSAL MIRSEDAGFV VITGVMSRRY LCMDFRGNIF GSHYFDPENC RFQHQTLENG YDVYHSPQYH FLVSLGRAKR AFLPGMNPPP YSQFLSRRNE IPLIHFNTPI PRRHTRSAED DSERDPLNVL KPRARMTPAP ASCSQELPSA EDNSPMASDP LGVVRGGRVN THAGGTGPEG CRPFAKFI Preparation: Produced from sera of rabbits immunized with highly pure Recombinant Human FGF-23. Anti-Human FGF-23-specific antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and then biotinylated. Sandwich ELISA: To detect Human FGF-23 by sandwich ELISA (using 100 μL/well), a concentration of 0.25-1.0 μg/mL of this antibody is required. This biotinylated polyclonal antibody, in conjunction with PeproTech Polyclonal Anti-Human FGF-23 (500-P319) as a capture antibody, allows the detection of at least 2000-4000 pg/mL of Recombinant Human FGF-23. Western Blot: To detect Human FGF-23 by Western Blot analysis, this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1-0.2 μg/mL. When used in conjunction with compatible development reagents, the detection limit for Recombinant Human FGF-23 is 1.5-3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions. 500-P319BT-1MG will be provided as 2 x 500 μg
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. The product of this gene inhibits renal tubular phosphate transport. This gene was identified by its mutations associated with autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets, an inherited phosphate wasting disorder. Abnormally high level expression of this gene was found in oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia, a phenotypically similar disease caused by abnormal phosphate metabolism. Mutations in this gene have also been shown to cause familial tumoral calcinosis with hyperphosphatemia.
Specifications
| FGF23 | |
| Polyclonal | |
| PBS with no preservative | |
| Q9GZV9 | |
| FGF23 | |
| E.coli-derived, 25.5kDa Recombinant Human FGF-2. | |
| 50 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody |
| ELISA, Western Blot | |
| Biotin | |
| FGF23 | |
| ADHR; FGF; Fgf23; FGF-23; FGFN; Fibroblast growth factor; Fibroblast growth factor 23; Fibroblast growth factor 23 C-terminal peptide; Fibroblast growth factor 23 N-terminal peptide; HPDR2; HYPF; Phosphatonin; PHPTC; tumor-derived hypophosphatemia inducing factor; Tumor-derived hypophosphatemia-inducing factor; UNQ3027/PRO9828 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 8074 | |
| -20°C | |
| Lyophilized |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.