Learn More
Invitrogen™ Claudin 2 Monoclonal Antibody (12H12)

Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Brand: Invitrogen™ 325600
Description
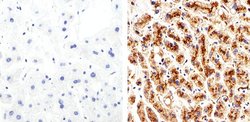
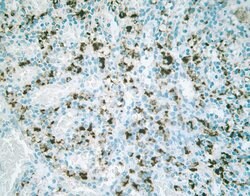
This antibody reacts specifically with the ~22-23 kDa Claudin-2 protein. Reactivity has been confirmed with human, mouse, rat, and dog liver and kidney homogenates, as well MDCK and Caco-2 cell lysates, by western blotting and immunfluorescence. Reactivity has also been confirmed with formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) human normal colon, spleen, and thyroid, and colon and breast cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry. For best results in immunohistochemistry (1-2 μg/mL) with formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues, heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER) with EDTA buffer, pH 8.0, is required prior to staining. In western blotting a non-specific band at 27 kDa is observed in some lysates. In Caco-2 cells this band appears stronger than the correct band at 22 kDa. An alternative product, rabbit anti-Claudin-2 (Cat. No. 516100) may be used for western blotting of these lysates.
Tight junctions are specialized regions of cell-cell contact that are particularly abundant in luminal epithelial cell sheets. In freeze-fracture electron micrographs, tight junctions are visualized as belt-like bands of anastomosing sealing strands (TJ strands) that completely encircle the lateral surfaces of each cell. TJ strands on adjacent cells are presumed to interact with each other to form a sort of 'molecular gasket' that prevents ions, water and other molecules from leaking between cells and thus, from one side of the sheet to the other. In addition to this so-called 'barrier' function, the 'fence' function of tight junctions plays an important role in maintaining epithelial cell-polarity by blocking the diffusion of membrane proteins between apical (luminal) and basolateral cell surfaces. Confinement of, for example, the glucose symport to apical surfaces allows glucose to be transported vectorially from the lumen, through the cell, and into the bloodstream. Several peripheral membrane proteins are associated with tight junctions including ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3 (members of membrane-associated guanylate-kinase family), cingulin, the 7H6 antigen, Rab-3b, symplekin. While their precise functions are not known, roles for these proteins have been suggested in tight junction assembly and maintenance; signal transduction; and the regulation of tight junction permeability. Furthermore, a growing body of evidence suggests that actin filaments play a major role in regulating tight junction permeability. Until recently, the only transmembrane protein known to be associated with tight junctions was occludin, an ~65 kDa protein with four transmembrane domains. Despite widespread expectation, a critical structural role for occludin in TJ strands was ruled out by the observation of apparently normal tight junctions formed between cells disrupted at both occludin alleles. Fortunately, a closer examination of isolated tight junctions uncovered two related ~22 kDa, four-transmembrane domain proteins, claudin-1 and claudin-2, with no similarity to occludin. In contrast to occludin, which induces only a small number of short strands at cell-cell contact sites when introduced into fibroblasts lacking tight junctions, claudin-1 and -2 induce networks of strands characteristic of true tight junctions. Though inconclusive, these findings suggest that claudin-1 and -2 are major structural components of TJ strands and that occludin plays some other accessory role. Excitement in the tight junction field continues to rise following the recent discovery of claudins -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, and -8 and experiments suggesting that tight junctions in different tissues are comprised of different sets of claudin family proteins. Claudin-1 and claudin-2 connect to the actin cytoskeleton through ZO-1; Claudin-2 functions as a paracellular channel with cation (Na+) selectivity at tight junctions. The expression of claudin-2 is restricted to the liver and kidney, with small amounts also found in the brain.
Specifications
| Claudin 2 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.5 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.1% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| O88552, P57739, Q95KM6 | |
| CLDN2 | |
| Synthetic peptide corresponding to a 26 amino acid sequence at the C-terminus of mouse Claudin-2. | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG2b |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot | |
| 12H12 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| CLDN2 | |
| AL022813; claudin 2; Claudin2; claudin-2; CLD2; Cldn2; integral membrane protein claudin-2; PSEC0059; RGD1560247; SP82; UNQ705/PRO1356 | |
| Mouse | |
| Protein A | |
| RUO | |
| 12738, 300920, 403649, 9075 | |
| -20°C | |
| Liquid |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.