Learn More
PeproTech CD14 (soluble) Polyclonal Antibody, PeproTech®, Invitrogen™
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Brand: PeproTech 500-P320-50UG
Description
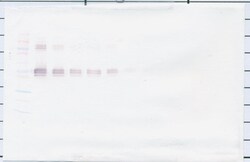
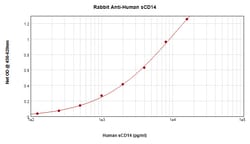
AA Sequence of recombinant protein: TTPEPCELDD EDFRCVCNFS EPQPDWSEAF QCVSAVEVEI HAGGLNLEPF LKRVDADADP RQYADTVKAL RVRRLTVGAA QVPAQLLVGA LRVLAYSRLK ELTLEDLKIT GTMPPLPLEA TGLALSSLRL RNVSWATGRS WLAELQQWLK PGLKVLSIAQ AHSPAFSCEQ VRAFPALTSL DLSDNPGLGE RGLMAALCPH KFPAIQNLAL RNTGMETPTG VCAALAAAGV QPHSLDLSHN SLRATVNPSA PRCMWSSALN SLNLSFAGLE QVPKGLPAKL RVLDLSCNRL NRAPQPDELP EVDNLTLDGN PFLVPGTALP HEGSMNSGVV P. Preparation: Produced from sera of rabbits immunized with highly pure Recombinant Human sCD14. Anti-Human sCD14-specific antibody was purified by affinity chromatography employing an immobilized Human sCD14 matrix. Sandwich ELISA: To detect Human sCD14 by sandwich ELISA (using 100 μL/well antibody solution) a concentration of 0.5-2.0 μg/mL of this antibody is required. This antigen affinity purified antibody, in conjunction with PeproTech Biotinylated Anti-Human sCD14 (500-P320Bt) as a detection antibody, allows the detection of at least 2000-4000 pg/mL of Recombinant Human sCD14. Western Blot: To detect Human sCD14 by Western Blot analysis this antibody can be used at a concentration of 0.1-0.2 μg/mL. Used in conjunction with compatible secondary reagents the detection limit for Recombinant Human sCD14 is 1.5-3.0 ng/lane, under either reducing or non-reducing conditions.
CD14 is a 55 kDa GPI-anchored glycoprotein that is constitutively expressed on the surface of mature monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. CD14 also serves as a multifunctional lipopolysaccharide receptor, and is released to the serum both as a secreted and enzymatically cleaved GPI-anchored form. CD14 binds lipopolysaccharide molecule in a reaction catalyzed by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), an acute phase serum protein. The soluble sCD14 can discriminate slight structural differences between lipopolysaccharides and is important for neutralization of serum allochthonous lipopolysaccharides by reconstituted lipoprotein particles. Further, CD14 has been shown to bind apoptotic cells, and can affect allergic, inflammatory and infectious processes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same CD14 isoform. Diseases associated with CD14 dysfunction include mycobacterium chelonae infection and Croup.
Specifications
| CD14 (soluble) | |
| Polyclonal | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Cd14 | |
| CD 14; CD14; CD14 antigen; CD14 molecule; cd14 monocyte; lipopolysaccharide receptor; lipoprotein receptor; LPSR antibody; monocyte differentiation antigen CD14; Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, membrane-bound form; Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, urinary form; monocyte differentiation antigen CD14; LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: monocyte differentiation antigen CD14; myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein; myeloid membrane glycoprotein precursor; sCD14; soluble CD14 | |
| Rabbit | |
| Antigen affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 929 | |
| -20°C | |
| Lyophilized |
| ELISA, Western Blot | |
| 0.1-1.0 mg/mL | |
| PBS with no preservative | |
| P08571 | |
| Cd14 | |
| HEK293 cells-derived Recombinant Human sCD14. | |
| 50 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.