Learn More
Cleaved PARP (Asp214) w/control Mouse anti-Human, Unlabeled, Clone: F21-852, BD
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody with Control
£236.00 - £379.66
Specifications
| Antigen | Cleaved PARP (Asp214) w/control |
|---|---|
| Clone | F21-852 |
| Concentration | 0.5mg/mL |
| Applications | Western Blot |
| Classification | Monoclonal |
| Product Code | Brand | Quantity | Price | Quantity & Availability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Code | Brand | Quantity | Price | Quantity & Availability | |||||
|
15846838
|
BD Biosciences
552596 |
50 μg |
£236.00
Each |
Please sign in to purchase this item. Need a web account? Register with us today! | |||||
|
15856838
|
BD Biosciences
552597 |
150 μg |
 £395.00 £379.66 / Each Save £15.34 3% Off |
Please sign in to purchase this item. Need a web account? Register with us today! | |||||
Description
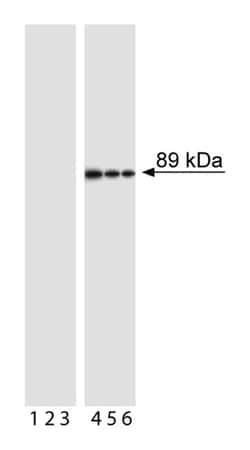
PARP (Poly [ADP-Ribose] Polymerase) is a 113-kDa nuclear chromatin-associated enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose units from NAD+ to a variety of nuclear proteins including topoisomerases, histones, and PARP itself. The catalytic activity of PARP is increased in cells following DNA damage, and PARP is thought to play an important role in mediating the normal cellular response to DNA damage. Additionally, PARP is a target of the caspase protease activity associated with apoptosis. The PARP protein consists of an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) and a C-terminal catalytic domain separated by a central automodification domain. During apoptosis, Caspase-3 cleaves PARP at a recognition site (Asp Glu Val Asp Gly) in the DBD to form 24- and 89-kDa fragments. This process separates the DBD (which is mostly in the 24-kDa fragment) from the catalytic domain (in the 89-kDa fragment) of the enzyme, resulting in the loss of normal PARP function. It has been proposed that inactivation of PARP directs DNA-damaged cells to undergo apoptosis rather than necrotic degradation, and the presence of the 89-kDa PARP cleavage fraction is considered to be a marker of apoptosis.
A peptide corresponding to the N-terminus of the cleavage site (Asp 214) of human PARP was used as the immunogen. The F21-852 monoclonal antibody reacts only with the 89-kDa fragment of human PARP-1 that is downstream of the Caspase-3 cleavage site (Asp214) and contains the automodification and catalytic domains. It does not react with intact human PARP-1. Cross-reactivity with other members of the PARP superfamily is unknown. Recognition of cleaved PARP in mouse cells has been demonstrated, and it may also cross-react with a number of other species due to the conserved nature of the molecule.
Specifications
| Cleaved PARP (Asp214) w/control | |
| 0.5mg/mL | |
| Monoclonal | |
| Mouse | |
| Cell Biology | |
| Aqueous buffered solution containing ≤0.09% sodium azide. | |
| IgG1 | |
| Affinity Purified |
| F21-852 | |
| Western Blot | |
| Unconjugated | |
| RUO | |
| Human | |
| Human cleaved PARP | |
| Primary | |
| Store undiluted at -20°C. |
For Research Use Only.
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.