Learn More
Invitrogen™ AHR Monoclonal Antibody (4MEJJ), PE-Cyanine7, eBioscience™

Rat Monoclonal Antibody
Brand: Invitrogen™ 25-5925-82
Description
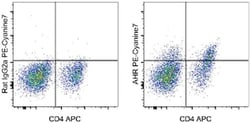
Description: This 4MEJJ monoclonal antibody recognizes mouse aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). The AHR is a ligand-activated transcription factor that mediates the toxic effects of a diverse group of environmental contaminants, most notably aryl hydrocarbons such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) and tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). The AHR has also been shown to bind to a number of naturally occurring compounds found in fruits and vegetables as well as compounds generated through normal cellular metabolism. AHR is localized in the cytoplasm in a complex that includes HSP90, p23, and XAP2/AIP/ARA9. Upon ligand-binding, AHR translocates to the nucleus and binds with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT), and this complex binds to the consensus DNA sequence, GCGTG, found in the promoter/enhancer regions of many genes such as CYP1A1. The AHR is expressed in many cell types, with highest expression levels found in liver. The AHR has been shown to play a role in the regulation/differentiation of Treg and Th17 cells. The 4MEJJ monoclonal antibody has been found to recognize the b-1, b-2 and d alleles of mouse AHR but does not cross-react with human AHR. Applications Reported: This 4MEJJ antibody has been reported for use in intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: This 4MEJJ antibody has been tested by intracellular staining and flow cytometric analysis of Th17-polarized mouse splenocytes using the Intracellular Fixatio...
AHR (Ah Receptor) belongs to a family of proteins comprised of its dimerization partner ARNT (HIF-1 Beta) and the Drosophila proteins PER and SIM. AHR contains an N-terminal sequence of approximately 200 amino acids termed the PAS domain. AHR, found in a variety of tissues, binds to a specific DNA enhancer sequence and initiates transcription of the mRNA for the cytochrome P-450 (CYPIA1) gene. The gene for AHR encodes a ligand-activated transcription factor involved in the regulation of biological responses to planar aromatic hydrocarbons. AHR has been shown to regulate xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes such as cytochrome P450, and its ligands included a variety of aromatic hydrocarbons. AHR is a ligand-activated helix/loop/helix transcription factor found in a variety of vertebrate species. The known ligands for AHR are foreign planar aromatic compounds, such as polycyclic aromatic compounds and halogenated aromatic compounds such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Unlike the steroid/thyroid hormone receptors, there is no known physiological ligand for AHR. Studies indicate that in non-ligand activated cells, AHR is found complexed with HSP90 predominantly in the cytoplasm. Upon binding to an agonist, the ligand-activated AhR is believed to transform to a nuclear, DNA binding form, and this transformation process appears to involve dissociation of HSP90 from AhR followed by formation of a heterodimer with AhR nuclear translocator protein (Arnt). Diseases associated with AHR include eosinophilic fasciitis and seborrheic dermatitis.
Specifications
| AHR | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.2 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| P30561 | |
| AHR | |
| E. coli derived, His-tagged AHR (aa 443-805). | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Mouse | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG2a κ |
| Flow Cytometry | |
| 4MEJJ | |
| PE-Cyanine7 | |
| AHR | |
| Ah; Ah receptor; Ahh; Ahr; Ahre; AH-receptor; aromatic hydrocarbon receptor; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; aryl-hydrocarbon receptor; bHLHe76; Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 76; dioxin receptor; In | |
| Rat | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 11622 | |
| 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE! | |
| Liquid |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.